Black as We Wanna Be
The Nation
2016-09-15
Matthew McKnight, Assistant Literary Editor
Stauffer, John, Zoe Trodd, and Celeste-Marie Bernier, Picturing Frederick Douglass: An Illustrated Biography of the Nineteenth Century’s Most Photographed American (New York: Liveright, 2015)
Fields, Karen E., and Barbara J. Fields, Racecraft: The Soul of Inequality in American Life (Brooklyn: Verso, 2012)
Trying to remedy racism on its own intellectual terrain is like trying to extinguish a fire by striking another match. The fiction must be unbelieved, the fire stamped out.
In her 2003 book Regarding the Pain of Others, Susan Sontag explored some questions about the ever-evolving technology of photography and what it does to us, particularly when it’s used to capture moments that would normally make us avert our eyes. “Perhaps the only people with the right to look at images of suffering of this extreme order,” Sontag wrote, “are those who could do something to alleviate it—say, the surgeons at the military hospital where the photograph was taken—or those who could learn from it. The rest of us are voyeurs, whether or not we mean to be.” Sontag spends much of the book discussing war photography; scant pages mention images and cruelties closer to home.
In the modern American context, there remains perhaps no more insidious cruelty than the belief—constantly manipulated and reinforced—that race is a natural and constant thing, something that should have any bearing on how we choose to organize our society and our lives. And though the convergence of racism and the photographic impulse isn’t new, the recent pictures and videos of killings by police officers have given renewed life to the questions that Sontag explored—and those she didn’t. Indeed, these images raise fewer questions about the act of looking at them than about the ways in which we view ourselves.
To modern eyes, the photographic portraits of Frederick Douglass are not so remarkable. Douglass was almost always photographed seated, wearing a dark suit, alternately staring directly into the camera and looking off to one side. As he abided by the portrait conventions of the era, only his skin color would have made these portraits remarkable in Douglass’s own time. The real joy of Picturing Frederick Douglass (2015)—a collection of 60 portraits, taken between 1841 and 1895; his four speeches on his theory of photography; and a critical essay by Henry Louis Gates Jr.—is to study his constancy. The changes in Douglass’s facial expressions across all of the portraits are mostly imperceptible: He looks serious, defiant, and proud.
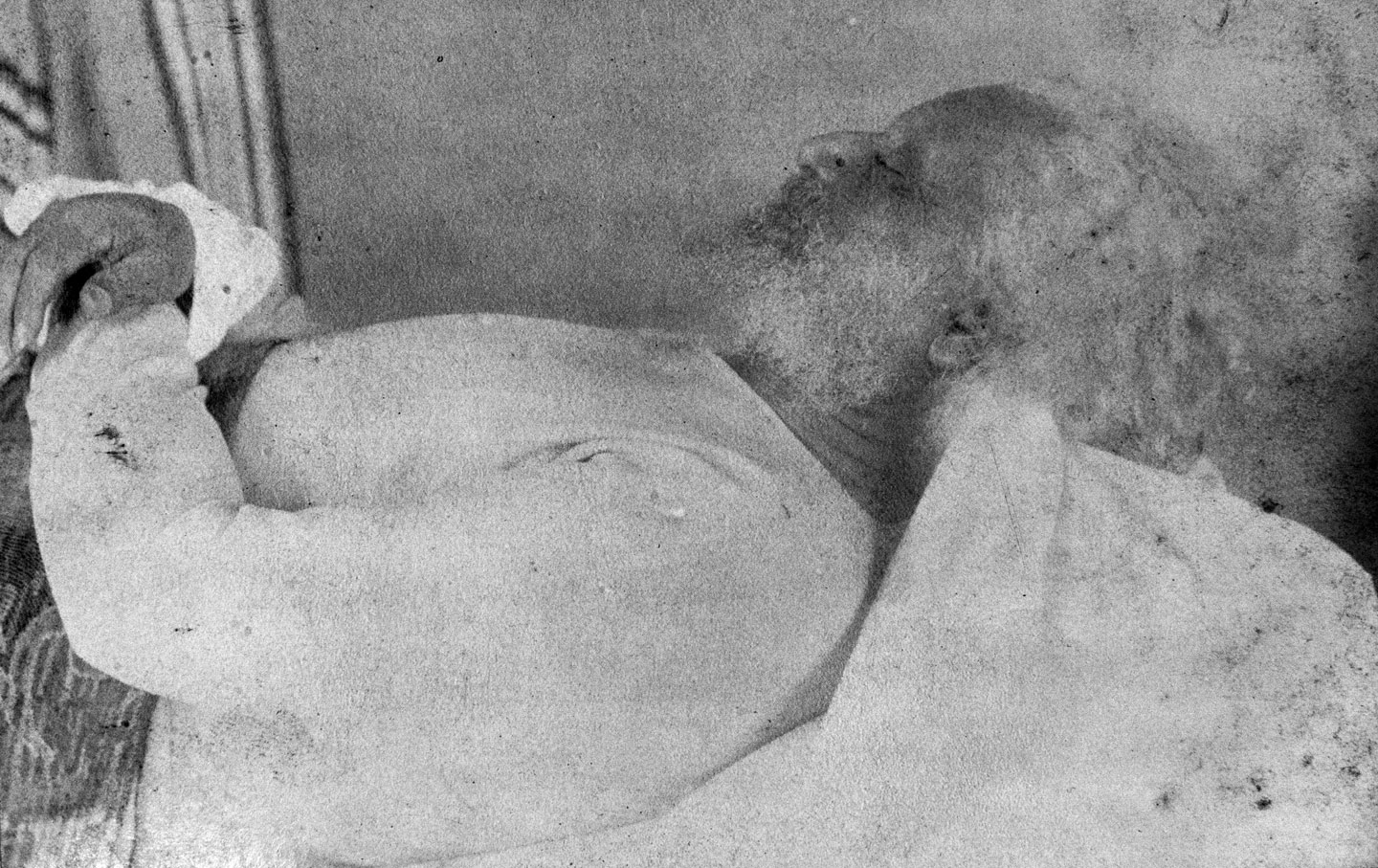
The final portrait of Douglass was taken on February 21, 1895. He’d died the day before. That image shows him lying on his bed in Washington, DC. It is mostly a spectral gray-white. His hair and beard, his clothes, the bed linens, and the wall in the background all appear to be about the same color. There’s a faint outline of his profile, and with his hands crossed over his abdomen, he looks as dignified as ever…
Read the entire article here.