“Gender is one of the most important predictors of racial identity, with women more likely than men to incorporate multiple races into their self-identification, all else being equal. This finding emerges across black-white, Asian-white, and Latino-white biracials, though the effect is most pronounced among black-white biracials. Biracial men are relatively more inclined to identify with their minority race, which can be attributed in part to the gendered nature of racial prejudice in the U.S. Men of all racial backgrounds are more likely to say they experience discrimination, and biracial men are more conscious than biracial women of their status in society as people of color.
Social class also consistently predicts how biracials identify. Put simply: “Money whitens.” Biracial people who grew up in more affluent families or in more affluent neighborhoods are more likely to identify as white and less likely to identify with their minority race. Higher incomes enable biracials to display external markers of wealth and increase their social mobility; when coupled with their mixed-race appearance, this can lead biracials to be perceived as white.
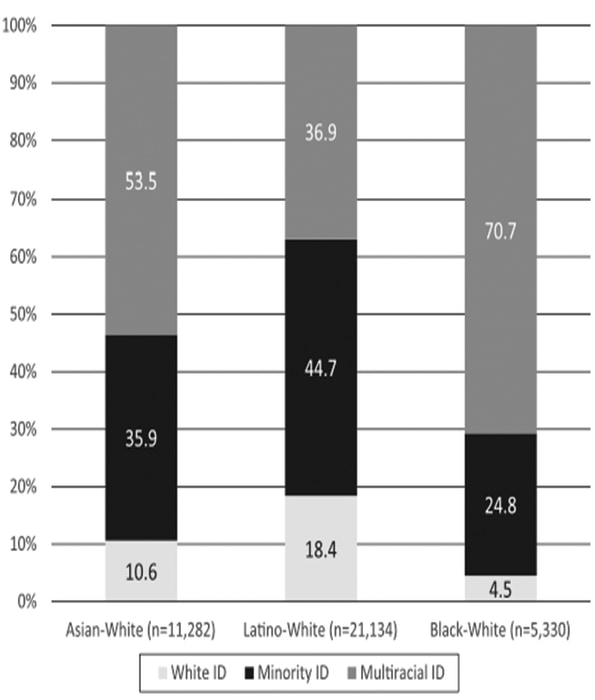
That said, relatively few biracial people identify as white – only 14 percent in my sample. Among black-white biracials, the rate is even lower: Just 5 percent identify as white. The category “white” does not extend to biracial blacks as it does to biracial Asians and Latinos.” —Lauren Davenport
Alex Shashkevich, “Stanford scholar examines biracial youth’s political attitudes and self-identification factors,” Stanford News, March 29, 2018. https://news.stanford.edu/2018/03/29/biracial-youths-political-views-self-identification-examined/.