Slavery’s legacies
The Economist
2016-09-10
SÃO PAULO
American thinking about race is starting to influence Brazil, the country whose population was shaped more than any other’s by the Atlantic slave trade
ALEXANDRA LORAS has lived in eight countries and visited 50-odd more. In most, any racism she might have experienced because of her black skin was deflected by her status as a diplomat’s wife. Not in Brazil, where her white husband acted as French consul in São Paulo for four years. At consular events, Ms Loras would be handed coats by guests who mistook her for a maid. She was often taken for a nanny to her fair-haired son. “Brazil is the most racist country I know,” she says.
Many Brazilians would bristle at this characterisation—and not just whites. Plenty of preto (black) and pardo (mixed-race) Brazilians, who together make up just over half of the country’s 208m people, proudly contrast its cordial race relations with America’s interracial strife. They see Brazil as a “racial democracy”, following the ideas of Gilberto Freyre, a Brazilian sociologist who argued in the 1930s that race did not divide Brazil as it did other post-slavery societies. Yet the gulf between white Brazilians and their black and mixed-race compatriots is huge…
…Of the 12.5m Africans trafficked across the Atlantic between 1501 and 1866, only 300,000-400,000 disembarked in what is now the United States. They were quickly outnumbered by European settlers. Most whites arrived in families, so interracial relationships were rare. Though white masters fathered many slave children, miscegenation was frowned upon, and later criminalised in most American states.
As black Americans entered the labour market after emancipation, they threatened white incomes, says Avidit Acharya of Stanford University. “One drop” of black blood came to be seen as polluting; laws were passed defining mixed-race children as black and cutting them out of inheritance (though the palest sometimes “passed” as white). Racial resentment, as measured by negative feelings towards blacks, is still greater in areas where slavery was more common. After abolition, violence and racist legislation, such as segregation laws and literacy tests for voters, kept black Americans down.
But these also fostered solidarity among blacks, and mobilisation during the civil-rights era. The black middle class is now quite large. Ms Loras would not seem anomalous in any American city, as she did in São Paulo…
…Both black and white Brazilians have long considered “whiteness” something that can be striven towards. In 1912 João Baptista de Lacerda, a medic and advocate of “whitening” Brazil by encouraging European immigration, predicted that by 2012 the country would be 80% white, 3% mixed and 17% Amerindian; there would be no blacks. As Luciana Alves, who has researched race at the University of São Paulo, explains, an individual could “whiten his soul” by working hard or getting rich. Tomás Santa Rosa, a successful mid-20th-century painter, consoled a dark-skinned peer griping about discrimination, saying that he too “used to be black”.
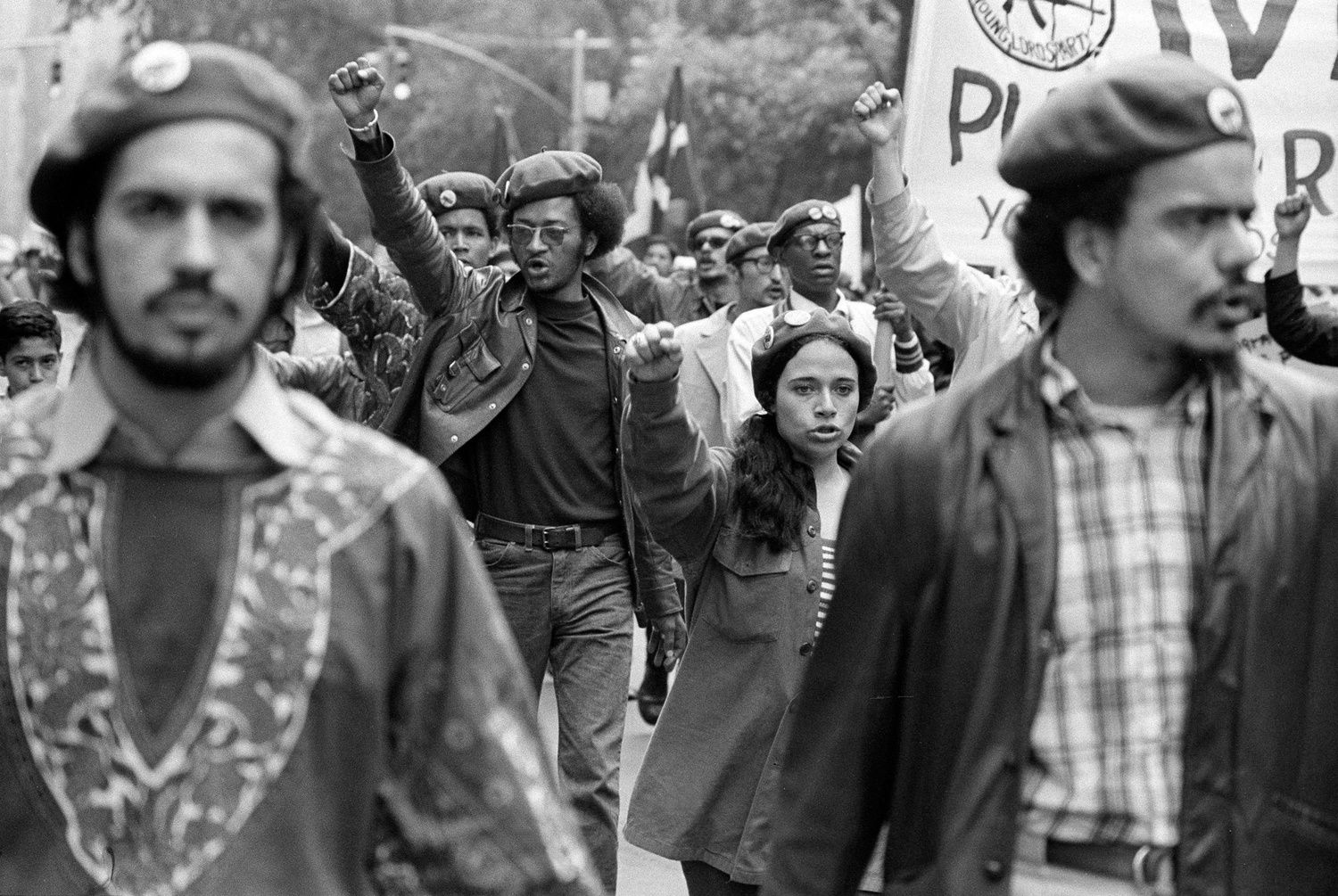
Though only a few black and mixed-race Brazilians ever succeeded in “becoming white”, their existence, and the non-binary conception of race, allowed politicians to hold up Brazil as an exemplar of post-colonial harmony. It also made it harder to rally black Brazilians round a hyphenated identity of the sort that unites African-Americans. Brazil’s Unified Black Movement, founded in 1978 and inspired by militant American outfits such as the Black Panthers, failed to gain traction. Racism was left not only unchallenged but largely unarticulated.
Now Brazil’s racial boundaries are shifting—and in the opposite direction to that predicted by Baptista de Lacerda. After falling from 20% to 5% between 1872 and 1990, the share of self-described pretos edged up in the past quarter-century, to 8%. The share of pardos jumped from 39% in 2000 to 43% in 2010. These increases are bigger than can be explained by births, deaths and immigration, suggesting that some Brazilians who used to see themselves as white or pardo are shifting to pardo or preto. This “chromatographic convergence”, as Marcelo Paixão of the University of Texas, in Austin, dubs it, owes a lot to policy choices…
Read the entire article here.