Brown Theology, Critical Race Theory, and the Laws of Burgos
Jesus for Revolutionaries
2015-06-29
Robert Chao Romero, Associate Professor of Chicana/o Studies and Asian American Studies
University of California, Los Angeles

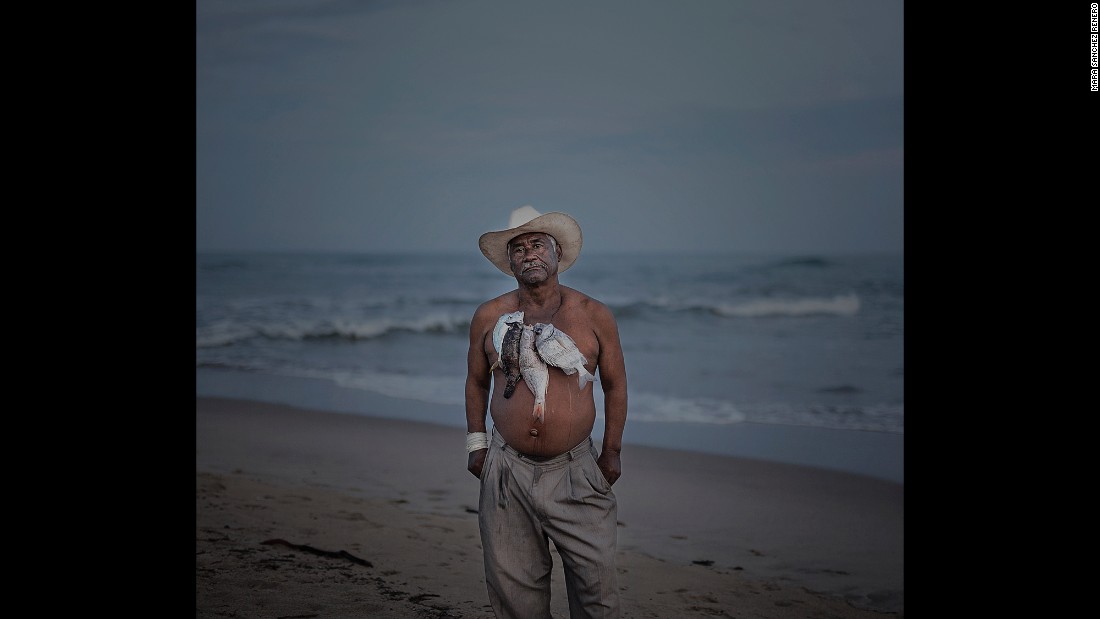
The fervent cries of Montesino soon reached the ears of King Ferdinand. On March 20, 1512, the king ordered Governor Diego Columbus to silence Montesinos under penalty of repatriation to Spain (Hanke, 18). On March 23, 1512, the Dominican Superior in Spain followed suit and likewise rebuked Montesinos and the rebellious monks for their irksome teaching. Undeterred, Montesinos held his ground. To break the impasse, both the colonists and Dominicans sent representatives to Spain to argue their positions before the royal court. The colonists appointed a Franciscan monk, Alonso del Espinal; the Dominicans selected Montesinos. (Hanke, 22, 23). Bewildered by the long list of abuses perpetrated against the natives, King Ferdinand convened a group of theologians and royal officials to examine the situation and to create laws which addressed the purported injustices.
In support of the colonist’s position, Friar Bernardo de Mesa asserted that the Indians should be subject to servitude because of their laziness. By forcing them to labor for Spaniards, de Mesa reasoned, it would “curb their inclinations and compel them to industry” (Hanke, 23). Drawing from Aristotle, a second court preacher, Licentiate Gregorio argued that forced labor was justified because the Indians were “natural slaves.”
According to Aristotle in Book 1 of the Politics, some human beings are born “natural slaves” (Smith, 110; 1254a21-24). Natural slaves lack reason and have an aptitude for manual labor (Smith, 110; Politics, 1260a12; 3.1280a33-34). Moreover, Aristotle asserts, a slave may be properly regarded as part of his master’s own body. (Smith, 110; Politics, 1254b20-23). In drawing from Aristotle’s natural slavery argument, Gregorio initiated a line of twisted theological reasoning which would later be used to justify conquest and colonization of all of the Americas, as well the enslavement of millions of African slaves. Because the diverse indigenous populations of North and South America were “natural slaves” some would argue, it was morally acceptable to conquer their lands and force them to labor for enlightened Europeans. As “natural slaves,” moreover, West Africans were less than human and therefore could be captured, shipped, and sold to Spanish, Portuguese, and English settlers.
After meeting more than 20 times, the royal junta came to several seemingly contradictory conclusions: 1. The Indians were free political subjects; 2. They were entitled to humane treatment; 3. Nonetheless, they could be subject to compulsory labor for Spaniards; and, 4. The Indians should be forced to live in close proximity to the Europeans in order to allow for more effective religious inculcation and instruction. (Hanke, 23). These principles became codified in the first racially discriminatory laws in the history of the Americas called the Laws of Burgos (Hanke, 24)…
Read the entire article here.